When it comes to optimizing your website for search engines, understanding the nuances of Technical SEO is important. So, what is Technical SEO? In simple terms, Technical SEO involves upgrading the technical elements of your website to improve how search engines crawl, index, and understand your content.
This aspect of SEO focuses on making your site quicker, more straightforward to navigate, and intelligible for search engines like Google. It encompasses everything from site speed and mobile responsiveness to security, structured data, and the overall infrastructure of your website. Essentially, Technical SEO ensures that your site is not just accessible but also crawlable and indexable by search engines, laying the foundation for better search engine rankings and an enhanced user experience.
Essential Technical SEO Elements
1. Ensure Website Uses HTTPS
One of the foundational elements of technical SEO is ensuring your website uses HTTPS. This secure protocol, indicated by the “S” in HTTPS, encrypts the data exchanged between your website and its users, protecting sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, and personal data.
Google has explicitly stated that HTTPS is a ranking signal, meaning websites using HTTPS may rank higher than those that do not. Additionally, HTTPS helps prevent man-in-the-middle attacks and improves website performance by eliminating the need for additional redirects, resulting in faster page loads and a better user experience.
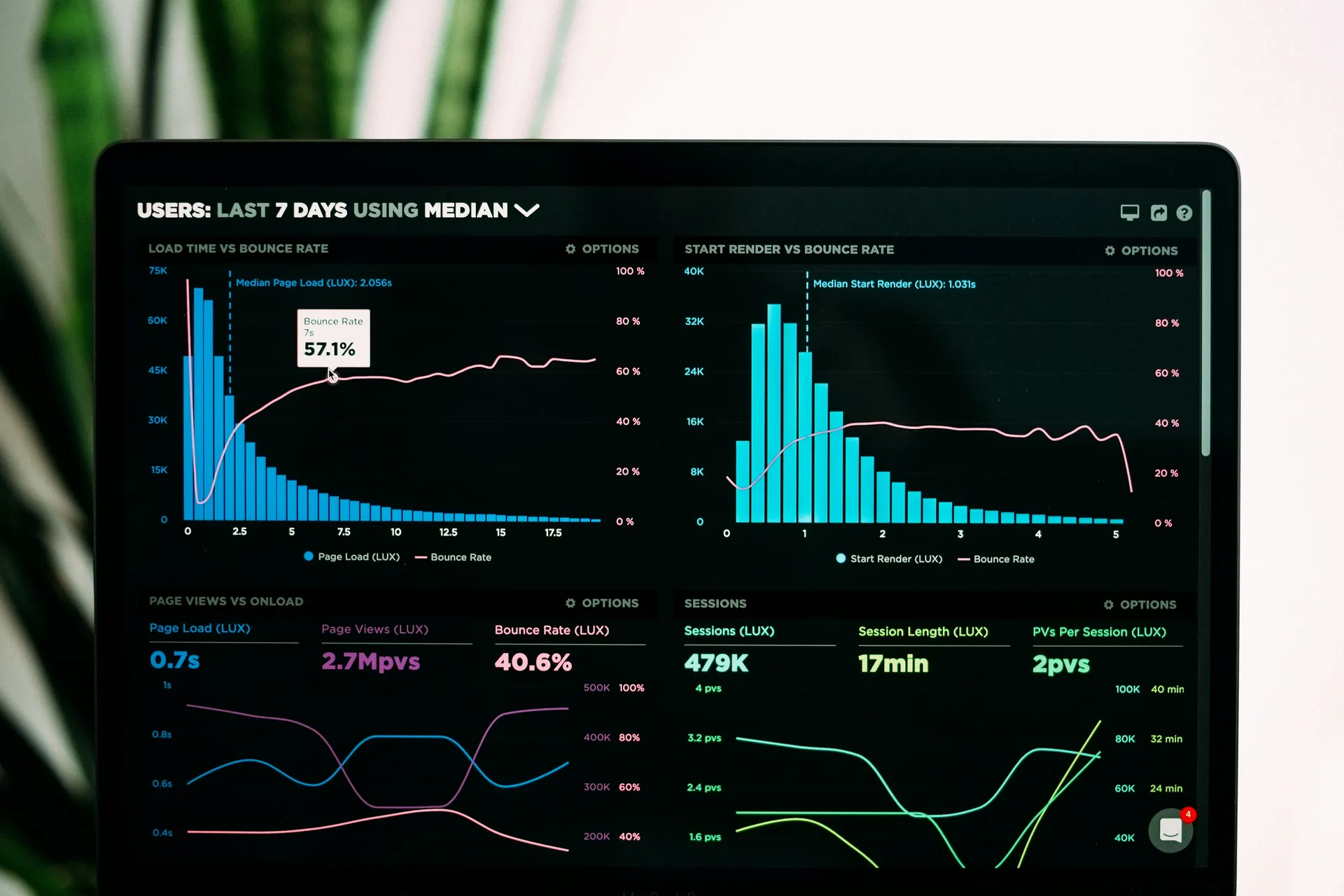
2. Optimize Website Speed
Website speed is a critical factor in technical SEO. A fast-loading website not only enhances user experience but also influences search engine rankings. Search engines prioritize websites that load quickly, as slow-loading sites can lead to higher bounce rates and lower engagement.
To optimize your website’s speed, consider optimizing images, using a content delivery network (CDN), and minifying your code. These actions can significantly reduce load times, ensuring your site remains engaging and accessible to both users and search engine crawlers.
3. Mobile Optimization
With the majority of internet traffic coming from mobile devices, ensuring your website is mobile-friendly is essential. A mobile-optimized website adapts to different screen sizes and devices, providing a seamless user experience.
Google favors mobile-friendly sites, and a responsive design can improve your search engine rankings. Mobile optimization includes ensuring that all elements of your site, such as buttons and menus, are easily accessible and usable on smaller screens.
4. Fix Duplicate Content Issues
Duplicate content can severely impact your website’s search engine rankings. When search engines encounter multiple versions of the same content, they may struggle to determine which version to index, leading to split ranking signals and reduced visibility. To address this, use canonical tags to specify the preferred version of a page.
This helps search engines understand which page is the original and should be indexed, avoiding penalties from Google’s Panda algorithm and ensuring your content is consistently presented to users.
5. XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is an essential tool for assisting search engines in understanding the structure of your website and locating all its pages. This file contains a list of all the URLs on your site that you want search engines to crawl and index. By submitting your XML sitemap to Google Search Console, you ensure that Google can effectively discover and index your content.
A properly maintained sitemap also plays a key role in identifying and resolving broken links and other crawl issues. Addressing these problems is important, as they can negatively impact your website’s visibility in search results.
Indexing and Crawling Optimization
6. Robots.txt File
A well-configured robots.txt file is essential for optimizing how search engines crawl and index your website. This file, located in the root directory of your site, provides instructions to search engine crawlers on which pages to crawl and which to avoid. By using “Allow” and “Disallow” directives, you can direct crawlers to focus on your most valuable content, prevent them from accessing large files or duplicate content, and conserve your crawl budget.
This ensures that search engines allocate their resources efficiently, indexing the pages that matter most to your business. It is important to place the robots.txt file in the correct location, update it with site changes, and avoid blocking essential assets like JavaScript and CSS files, which are necessary for proper page rendering.
7. Noindex Unimportant Pages
Noindexing unimportant pages is another key strategy in indexing and crawling optimization. Pages like login screens, thank you pages, or internal search results do not need to be indexed and can clutter your search engine results.
You can use the “noindex” directive in your robots.txt file or the meta robots tag on individual pages to prevent these pages from being indexed. This helps maintain a clean and relevant index of your site’s content, ensuring that users and search engines see only the pages that add value.
8. Structured Data Implementation
Implementing structured data, also known as schema markup, helps search engines understand the context and content of your website. This markup provides additional information about your pages, such as business hours, reviews, and event details, which can be displayed in search results as rich snippets. Structured data enhances the visibility of your site in search engine results pages (SERPs) and improves the user experience by providing more detailed information directly in the search results.
9. Hreflang Tags for Multilingual Content
If your website caters to a multilingual audience, using hreflang tags is vital for ensuring that the right content is served to the right users. Hreflang tags tell search engines which version of a page is intended for which language or region.
This helps in avoiding duplicate content issues and ensures that users are directed to the most relevant version of your content, improving both user experience and search engine rankings.
10. Check and Fix Broken Links
Broken links can significantly hinder your website’s performance and user experience. These links often lead to 404 errors, which not only frustrate users but also confuse search engine crawlers. Regularly checking for and fixing broken links is essential to maintain a healthy site structure.
Tools like Google Search Console and SEO audit tools can help identify broken links. By correcting them, you ensure that both users and search engines can navigate your site seamlessly.
Advanced Technical Considerations

11. Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics introduced by Google to measure the user experience of a web page. These metrics are important for understanding how users interact with your site and can significantly impact your search engine rankings.
The three main Core Web Vitals are:
– Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This measures the time it takes for the largest content element on your page to load. Aim for an LCP of less than 2.5 seconds to ensure a good user experience.
– Interaction to Next Paint (INP): This metric assesses how quickly your website responds to user interactions. A good INP score is 200 milliseconds or less, indicating a fast and responsive experience.
– Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): This measures the visual stability of your page, ensuring that elements do not shift unexpectedly as the page loads. A CLS score of less than 0.1 is ideal for a stable user experience.
Optimizing for Core Web Vitals can lead to faster loading times, more responsive interactions, and stable visual elements, all of which contribute to a positive user experience and improved search engine rankings.
12. Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a network of distributed servers that deliver web content to users based on their geographic location. Using a CDN can significantly improve your website’s speed and performance by reducing the distance between users and your website’s resources. This results in faster load times, lower latency, and an overall better user experience.
Additionally, CDNs can help distribute the load on your server, making your site more resilient to traffic spikes and reducing the risk of downtime.
13. Implement AMP
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) is a project aimed at making web pages load faster on mobile devices. Implementing AMP involves creating lightweight versions of your web pages that are optimized for mobile performance. AMP pages are designed to load quickly, even on slow networks, which can improve user engagement and reduce bounce rates.
Google also favors AMP pages in mobile search results, which can enhance your site’s visibility and drive more traffic to your mobile site.
14. Manage Redirects
Redirects are essential for maintaining a clean and user-friendly website, especially when you need to move content or change URLs. However, mismanaged redirects can lead to crawl errors, slow down your site, and negatively impact user experience.
Ensure that you use the correct types of redirects (301 for permanent changes and 302 for temporary changes) and test them regularly to avoid broken links and crawl issues. Tools like Google Search Console can help you identify and fix redirect problems efficiently.
15. Regular SEO Audits
Regular SEO audits are essential for maintaining and improving your website’s technical SEO. An SEO audit involves a detailed examination of your site’s structure, content, and technical elements to pinpoint issues such as broken links, duplicate content, slow page speeds, and other technical problems.
Using tools like Google Search Console, Google Pagespeed Insights, and specialized SEO audit software can simplify the process and ensure accuracy. By addressing the issues uncovered during an audit, you can keep your site optimized for search engines while delivering a seamless user experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, technical SEO serves as the backbone of a successful online presence, ensuring your website is optimized for both search engines and users. Key points to remember include the importance of a secure HTTPS protocol, optimized website speed, and a mobile-friendly design.
Core Web Vitals, such as Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Interaction to Next Paint (INP), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), are essential for enhancing user experience and boosting search engine rankings. Properly configuring robots.txt files, avoiding duplicate content, and implementing structured data also play vital roles in technical SEO. Regular SEO audits and maintaining a clean site structure with clear internal linking are essential practices to follow.
By addressing these technical aspects, you can significantly improve your website’s visibility, user engagement, and overall search engine performance. Take action today by implementing these strategies to enhance your website’s technical SEO, driving more organic traffic and conversions.
FAQ
What is the importance of site speed in technical SEO, and how can I optimize it?
Site speed is important in technical SEO as it directly influences search engine rankings, user satisfaction, and engagement. To optimize site speed, use advanced caching techniques, optimize and compress images, implement lazy and asynchronous loading, consider Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP), and optimize server and hosting settings.
These strategies reduce load times, enhance user experience, and improve crawlability and indexing by search engines.
How do I create and submit an XML sitemap to improve my website’s indexing?
To create an XML sitemap, gather all your website’s URLs, either manually, using a crawler like Screaming Frog, or from Google Analytics. Code the URLs in XML format using tags like “, “, “, and optional tags like “, “, and “.
Submit the sitemap to Google Search Console by signing in, clicking “Sitemaps” in the left sidebar, adding the sitemap URL, and clicking “Submit.”
What are the common technical SEO issues that can lead to Google penalties, and how can I avoid them?
Common technical SEO issues that can lead to Google penalties include:
- Keyword Stuffing and Hidden Text: Avoid overloading pages with keywords and using hidden text. Use keywords naturally and ensure all text is visible to users.
- Cloaking and Sneaky Redirects: Do not show different content to users and search engines. Ensure redirects lead to intended pages and avoid misleading users.
- Structured Data Issues: Follow Google’s Rich Snippets guidelines and ensure markup is accurate and visible to users. Correct any errors in structured data to avoid penalties.
- AMP Content Mismatch: Ensure the AMP version of a page matches its non-AMP counterpart to avoid confusing users and triggering penalties.
- Thin Content: Provide high-quality, original content that adds value to users. Avoid auto-generated, scraped, or low-quality content.
- Unnatural Links: Remove or modify links that are artificial, deceptive, or manipulative. Use the
rel="nofollow"attribute if necessary.
How can I use structured data to enhance my website’s visibility in search engine results?
To enhance your website’s visibility in search engine results using structured data, add schema markup to your HTML code. This markup helps search engines understand your content better, making your site eligible for rich results such as FAQs, product reviews, and event listings. Use formats like JSON-LD, microdata, or RDFa, and ensure the markup represents the main content of your page.
This can improve your click-through rates and make your listings more appealing in search engine results pages (SERPs).
